Basic Components used in Electronics Circuits
In electronics, circuits are constructed using a variety of basic components, each serving specific functions. Here's a detailed description of some of the most commonly used components:
1. Resistor
Function: Resistors limit the flow of electric current, providing a specific amount of resistance measured in ohms (Ω).
Description: A resistor is a passive component that opposes the flow of electric current, thereby controlling the voltage and current within the circuit. The resistance value is indicated by colour codes or numbers printed on the resistor body. Resistors come in various forms, such as fixed, variable (potentiometers), and thermistors (temperature-dependent resistors).
2. Capacitor
Function: Capacitors store and release electrical energy in a circuit, measured in farads (F).
Description: A capacitor consists of two conductive plates separated by an insulating material called a dielectric. They can block DC currents while allowing AC signals to pass, making them useful for filtering, coupling, and decoupling applications. Capacitors come in various types, such as ceramic, electrolytic, and tantalum, each suited for different applications.
3. Inductor
Function: Inductors store energy in a magnetic field when electrical current flows through them, measured in henries (H).
Description: An inductor is a coil of wire, often wound around a core made of ferrite or iron, that creates a magnetic field as current flows through it. Inductors resist changes in current, making them useful for filtering signals, tuning circuits, and energy storage in power supplies.
4. Diode
Function: Diodes allow current to flow in only one direction, offering rectification capabilities.
Description: A diode is a semiconductor device with two terminals: an anode and a cathode. When a forward voltage is applied, current flows from the anode to the cathode, but not in the reverse direction. Types of diodes include standard rectifier diodes, Zener diodes (for voltage regulation), and light-emitting diodes (LEDs).
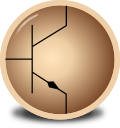
5. Transistor
Function: Transistors amplify electrical signals and can act as switches.
Description: A transistor is a semiconductor device with three terminals: emitter, base, and collector (for bipolar junction transistors, BJT) or source, gate, and drain (for field-effect transistors, FET). By applying a small current or voltage to one terminal (base or gate), a larger current can be controlled between the other two terminals, enabling signal amplification and switching functions.
BJT
MOSFET
< Basic Components used in Electronics Circuits up Different kinds of Analysis >